In our article “Gorodki” we will tell you about the Russian game, which has developed into a horodoshny sport. You will learn a brief history, rules and features of the game.
History of Gorodki
“Russian bowling” – that’s what else calls horodoshny sport, it has at least 200 years of history and originated exclusively in our country. By the beginning of the 19th century, the game of horodki was widespread throughout Russia, it was played by Russian writers (L. Tolstoy, M. Gorky), statesmen (Nicholas II, V. Lenin, I. Stalin) and even Russian commanders (A. Suvorov).
Gorodki is an all-season Russian game in which the throwing of a bat is necessary to knock out of the limits of the markings of figures made of wooden cylinders (gorodki).
The first rules of the game were formed and described by Archbishop Theophanes in the 18th century, and in the early 19th century the game moved from the village to the city limits. In the city the marking for the game was transformed, it acquired a modern form (2*2 meters), and the game began to be played in specially designated places.

August 19, 1923 became the date of birth of the USSR Federation of Horodoshny Sport. On this day the first USSR championship was held in Moscow, which gave further impetus to the popularization of the game.
In 1933, the updated rules of the game were published: 15 of 220 well-known figures were chosen to be used in the classic game; the grounds began to be built of hard materials (concrete, asphalt); the game began to use bats with metal inserts.
Since 1936, the popularization of the game has been going by leaps and bounds, as Russia began to hold individual and team championships, and athletes were awarded sports ranks, titles and qualifications.
The game of gorodki gained its peak popularity in the 50-70s of the 20th century. It became the third most popular sport in the USSR after soccer and hockey. Gorodki was so popular in Russia that stadiums, pioneer camps, recreation centers without a simple ground for playing gorodki simply did not build. All the factories had their own stadiums and, of course, playgrounds for playing gorodki.
According to statistics, during this period about 600,000 people played the game, and in one major city alone there were several dozen clubs in which sports dynasties were formed.
The decline in interest in the game occurred in the early 80s, when this sport was not presented at the home Olympics, and it began to be perceived by people as “having no prospects”. In 1993, an international federation (IFGS) was established with 12 countries as members. Since the early 2000s, interest in the game has gradually returned, with annual world championships and European Cup competitions.
Rules of Gorodki
The aim of the game is to use a special bat to knock out completely the figures from the “city” (a platform on which there are wooden cylinders called “gorodki”) for the smallest number of throws.
There are several types of bats: Children’s (up to 800 grams) and Adult (up to 2 kg). Bat for the player is something like a relic, everyone customizes it with the help of inserts strictly personal to himself. In professional players, the weight of the bat can reach up to 3.5 kg. But why increase the weight?
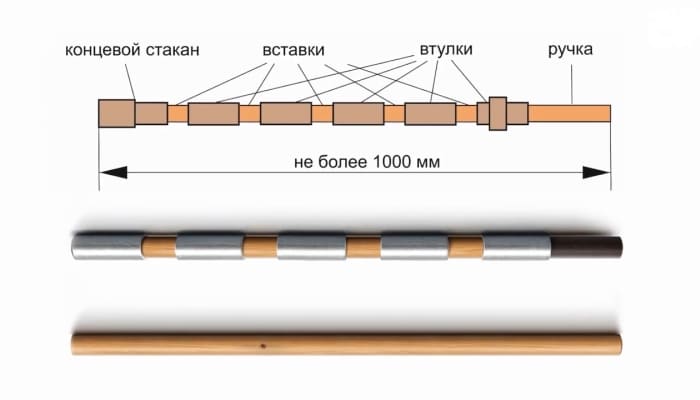
In the game, the center of gravity of the bat is essential, its location plays a significant role in the setting of the throw, achieving its stability. From the location of the center of gravity depends on the flight of the bat.
Game progress: Players take turns making 2 throws. The first throw on any figure is made from the cone (13 meters), as soon as one town (wooden cylinder) is knocked out, the other throws, if they are required, are made from the semi-con (6.5 meters). The exception is the final 15th figure “Letter”, as it is thrown only from the cone.
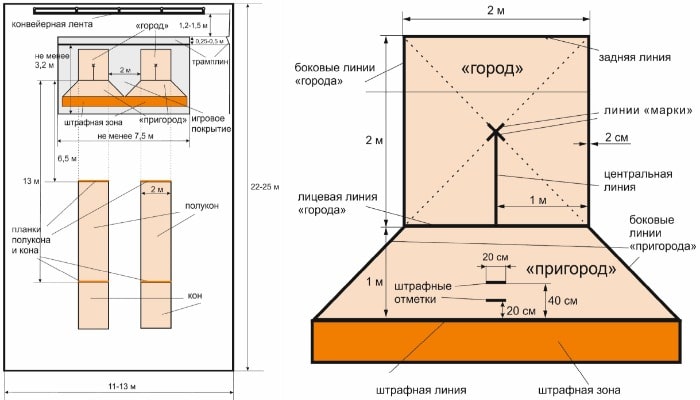
A figure is considered knocked out if it is completely outside the square (city) and suburban. The size of the city is 2m by 2m. In the classic version of the game, a round consists of 15 pieces, which are lined up sequentially. The main task is to spend the least number of throws to knock out all the pieces.

In some cases, the throw is considered lost (the throw is not counted, the gorodki are restored to their former place). For example, when stepping over the line during a throw, as well as if the bat touched the penalty line or sand in the penalty area.
If the gorodok hits the penalty area after being hit, a penalty stroke is awarded. Gorodok is placed in the suburbs at the penalty mark of 20 cm if one gorodok has been knocked out of the figure, or at 40 cm if no gorodoks have been knocked out of the figure. It requires real professionalism to take a penalty shot without hitting the penalty area with the bat.
If a knocked-out gorodok returns to the city or suburb (rolls back), it is considered knocked out. A gorodok is considered knocked out if it has completely left the “city” or “suburb” zone in any direction without touching the penalty zone.
In case of equality of throws in individual competitions, the winner is determined by the number of throws spent on the last figure, penultimate figure or by the number of throws spent on specific figures: “Shooting gallery”, ” Watchmen”, “Machine gun installation” and “Letter”.
In case of equality of throws in team competitions, the game is considered a draw. The team that wins two out of three games and 3 games in a five-set match wins.
Figures of Gorodki
Figures in gorodki are knocked out in a certain sequence. This sequence and the correct placement of the figures are shown below.
The first to be knocked out is “Cannon”, the second is “Fork”, the third is “Star”, the fourth is “Arrow”, the fifth is “Well”, the sixth is “Crankshaft”, the seventh is “Artillery”, the eighth is “Racquet”, ninth – “Machine Gun installation”, tenth – “Lobster”, eleventh – “Watchmen”, twelfth – “Sickle”, thirteenth – “Shooting gallery”, fourteenth – “Airplane”, and fifteenth – “Letter”.
Where can I play in gorodki? On the website of the Russian Federation of Horodoshny Sport there is a map of sites. Among the regions are Altai Krai, Moscow, the Republic of Crimea, the Samara region, St. Petersburg, etc. The contact details of the responsible officials are given. Moreover, there are contact details of responsible people who can be called to sign up for lessons. At the sites there is a trainer who professionally deals with both children and adults.